In the production process of frosted acrylic sheet, how to control the thickness and roughness of the frosted layer to meet the needs of different customers?
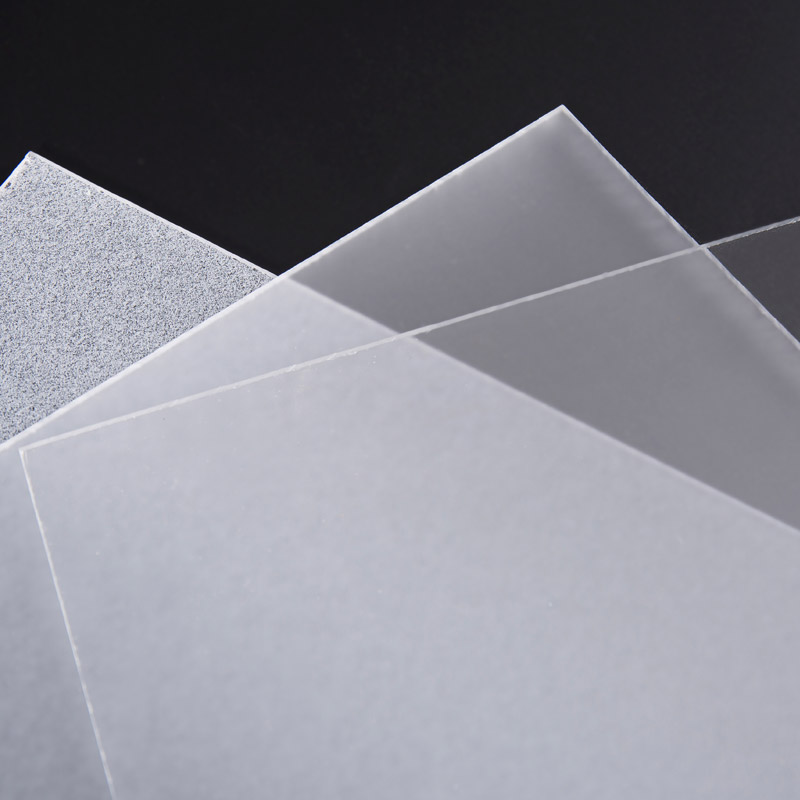
Frosted acrylic sheet, with its unique texture and wide application, occupies an important position in modern decorative and functional materials. In the production process, controlling the thickness and roughness of the frosted layer to meet the needs of different customers is a key technology. The following are some common control methods:
Control of frosted layer thickness
Abrasive selection and ratio: Abrasives of different particle sizes have a direct impact on the thickness of the frosted layer. Generally speaking, abrasives with larger particle sizes remove materials faster during the grinding process, which will increase the thickness of the frosted layer relatively significantly; while abrasives with smaller particle sizes can achieve more delicate grinding, and the thickness of the frosted layer increases relatively slowly. For example, when producing products that require a thicker frosted layer, the proportion of large particle size abrasives can be appropriately increased. At the same time, the ratio of abrasives to other additives will also affect the frosting effect and thickness. By adjusting the concentration of abrasives in the grinding liquid, the contact frequency and action intensity of the abrasives with the surface of the acrylic sheet can be controlled, thereby controlling the thickness of the frosted layer.
Grinding time and speed: Grinding time is an important factor affecting the thickness of the frosted layer. Extending the grinding time increases the time that the abrasive acts on the surface of the acrylic plate, which will gradually thicken the frosted layer. However, too long a grinding time may cause the frosted layer to be too thick, affecting the light transmittance and other properties of the plate, so it is necessary to accurately control the grinding time according to the customer's specific requirements for the thickness of the frosted layer. In addition, the grinding speed is also related to the thickness of the frosted layer. A higher grinding speed can make the abrasive act on the surface of the acrylic plate more quickly, increasing the thickness of the frosted layer in the same time. However, too fast a speed may make the thickness of the frosted layer uneven, so it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as equipment performance, abrasive characteristics and plate material to select a suitable grinding speed.
Grinding equipment parameter adjustment: Some parameters of the grinding equipment are crucial to the control of the frosted layer thickness. For example, the pressure of the grinding head affects the contact pressure between the abrasive and the surface of the acrylic plate. Increasing the pressure will cause the abrasive to cut deeper into the surface of the plate, accelerating the formation and thickening of the frosted layer, but excessive pressure may cause scratches or deformation on the surface of the plate. In addition, the rotation frequency of the grinding head will also affect the thickness of the frosted layer. A higher rotation frequency can make the abrasive more evenly distributed on the surface of the plate, which helps to form a uniform frosted layer, but it will also accelerate the thickening speed of the frosted layer to a certain extent. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately adjust the parameters such as the pressure and rotation frequency of the grinding equipment according to the actual production situation to achieve effective control of the thickness of the frosted layer.
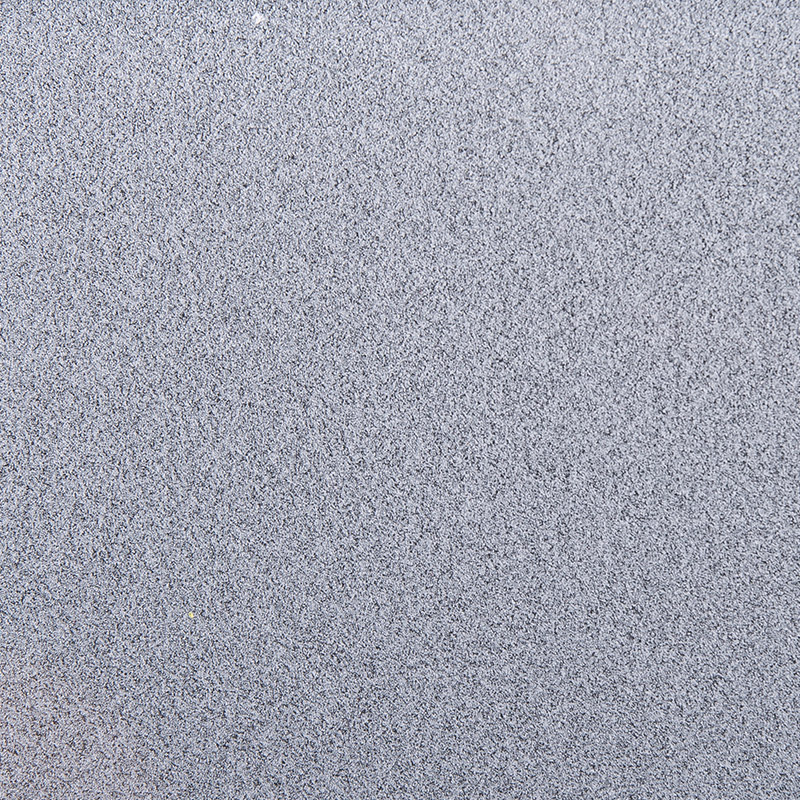
Control of the roughness of the frosted layer
Selection of abrasive characteristics: The characteristics such as the type, shape and hardness of the abrasive play a key role in the roughness of the frosted layer. Different types of abrasives, such as aluminum oxide and silicon carbide, have different hardness and cutting ability, which will produce different frosting effects. Abrasives with higher hardness can leave more obvious scratches on the surface of the acrylic plate, increasing the roughness of the frosted layer; while abrasives with lower hardness can achieve a more delicate frosting effect and reduce the roughness. In addition, the shape of the abrasive will also affect the roughness. Angular abrasives will make the surface of the frosted layer relatively rough, while rounded abrasives can make the surface of the frosted layer smoother. Therefore, according to the customer's requirements for roughness, choosing the right type and shape of abrasive is an important part of controlling the roughness of the frosted layer.
Grinding process optimization: Different links of the grinding process have a significant impact on the roughness of the frosted layer. In the pre-grinding stage, the use of coarser abrasives and greater grinding force can quickly remove the unevenness of the plate surface, laying the foundation for subsequent fine grinding, but this will make the surface roughness relatively high. In the fine grinding stage, it is necessary to use finer abrasives and smaller grinding forces to further process the pre-grinded surface to reduce the roughness and make the frosted layer reach the fineness required by the customer. In addition, the grinding method will also affect the roughness. For example, the use of circular motion grinding may make the scratches on the surface of the frosted layer more uniform and the roughness relatively low; while the linear motion grinding method may leave some obvious linear scratches, which increases the roughness. Therefore, according to the specific requirements of the customer for roughness, optimizing the grinding process and selecting the appropriate grinding stage parameters and grinding methods are effective means to control the roughness of the frosted layer.
Post-processing process: The post-processing process is also very important for adjusting the roughness of the frosted layer. Common post-processing methods include chemical polishing and surface coating treatment. Chemical polishing is to soak the frosted acrylic sheet in a specific chemical solution to dissolve the microscopic protrusions on the surface of the sheet, thereby reducing the roughness and improving the surface flatness. Surface coating treatment is to apply a thin layer of transparent coating on the surface of the frosted layer, which can not only protect the frosted layer, but also fill the tiny depressions on the surface to a certain extent, making the frosted layer look more delicate and reducing the roughness. By selecting appropriate chemical polishing solutions and process parameters, as well as optimizing the formulation and coating process of the surface coating, the roughness of the frosted layer can be fine-tuned according to customer needs to achieve the desired effect.
In the production process of frosted acrylic sheets, to accurately control the thickness and roughness of the frosted layer, it is necessary to comprehensively consider multiple factors such as abrasive selection, grinding process, equipment parameter adjustment, and post-processing process. The cast acrylic sheets produced by Hangzhou Oleg International Trading Co., Ltd. adopt precise system integration control, which not only ensures high production, but also reliable quality. Its product quality not only meets but even exceeds the GB/T7134-2008 quality product standard. Whether it is single-sided frosted acrylic sheet or double-sided frosted acrylic sheet, Oleg can provide professional solutions for bulk buyers from all walks of life to meet their unique needs for frosted acrylic sheet in thickness, roughness and other properties, and become the preferred manufacturer of high-quality cast acrylic sheet for customers.